Gen Z stereotypes debunked: Surprising new research findings
Think you know Gen Z in the workplace? Think again. Marlee's groundbreaking study dives deep into common stereotypes, uncovering surprising truths and revealing how this generation is reshaping the future of work. Prepare to have your assumptions challenged.
- Author
Marlee

Generation Z (Gen Z) has become a hot topic of discussion, often surrounded by a cloud of stereotypes and misconceptions. Born between 1997 and 2012, this generation is now entering the workforce, bringing unique values, skills, and perspectives. But how much of what we think we know about Gen Z is actually true?
Let's explore Gen Z stereotypes, challenge some common misconceptions, and highlight three key strengths for Gen Z in the workplace from groundbreaking new research from Marlee's Gen Z at Work Study.
The Gen Z stereotype phenomenon
Before we delve into specific stereotypes, it's crucial to understand why stereotypes exist and how they impact our perceptions. Stereotypes are mental shortcuts our brains use to categorize and make sense of the world. While they can sometimes be based on kernels of truth, they often oversimplify complex realities and can lead to unfair judgments.
For Gen Z, these stereotypes have been shaped by a unique set of circumstances:
- They're the first true digital natives born into a world of smartphones and social media.
- They've grown up in an era of global uncertainty, including economic recessions and a global pandemic.
- They're the most diverse generation in history, with different values and expectations than their predecessors.
These factors have contributed to various stereotypes about Gen Z in the workplace, which Gen Z says is holding them back. We'll now explore and challenge some of these stereotypes.
Top 4 Gen Z stereotypes in the workplace
1. "Entitled and expecting instant gratification"
This stereotype suggests that Gen Z workers expect immediate rewards and recognition without putting in the necessary work. However, Marlee's Gen Z at Work study paints a different picture.
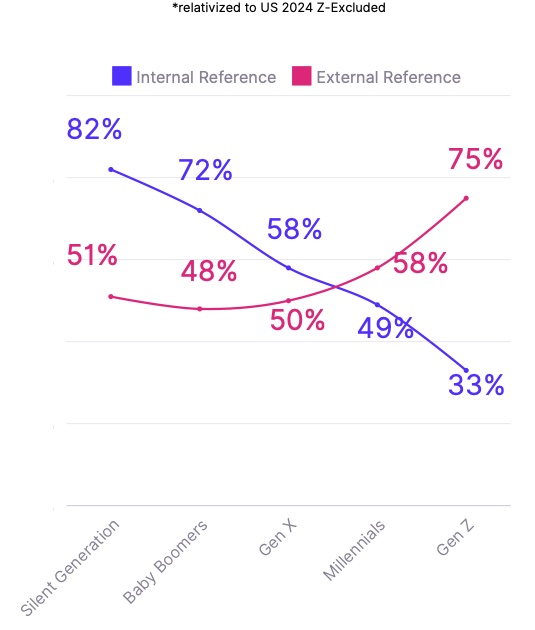
Reality: While Gen Z values feedback and recognition, it's not about entitlement. The study found that Gen Z has a 47% increase in seeking external feedback compared to previous generations. From onboarding to leadership development, Gen Z needs to be paired with someone who can offer immediate feedback on their performance. Remote setups can make this challenging, so it’s vital companies install the right tools and tech to facilitate greater connection and opportunities for real-time feedback across teams.
A 47% increase in seeking others’ opinions before their own
2. "Tech-addicted and lacking interpersonal skills"
The assumption here is that Gen Z's digital upbringing has left them ill-equipped for face-to-face interactions in the workplace.
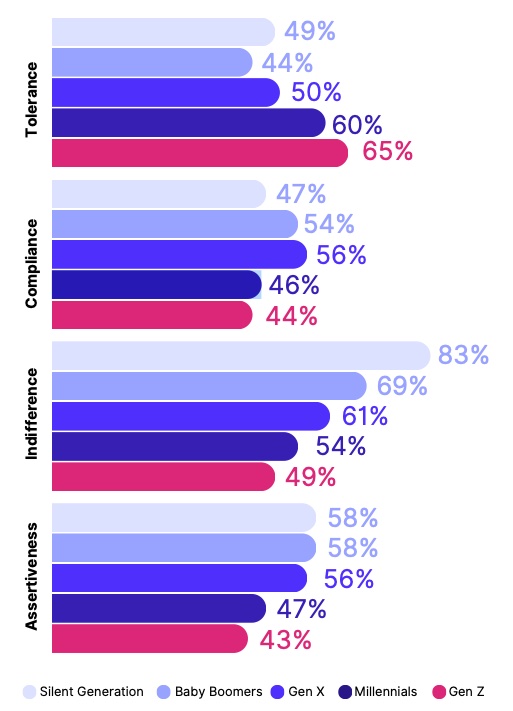
Reality: While it's true that Gen Z is comfortable with technology, this doesn't necessarily translate to poor interpersonal skills. Earlier generations are more motivated by job titles, achievement and walking to the beat of their own drum. Creativity and innovation are the dominant flavor of their working lives, coupled with a deep interest in the inner emotional worlds of their teammates and roles that expand their knowledge.
Later generations, however, place greater importance on inclusivity, a trend that’s increased by 33% across the generations.
They desire workplaces that are authentic and make it safe for everyone to be themselves, working in ways that bring out their best. So much so, that they’ll actively seek out a sense of belonging in prospective workplaces. It’s a noticeable shift from ‘me’ to ‘we’ at work also reflected in the findings.
Later generations place greater importance on inclusivity, a trend that’s increased by 33% across the generations
3. "Job-hoppers with no loyalty"
This stereotype paints Gen Z as fickle employees who will jump ship at the first sign of a better opportunity.
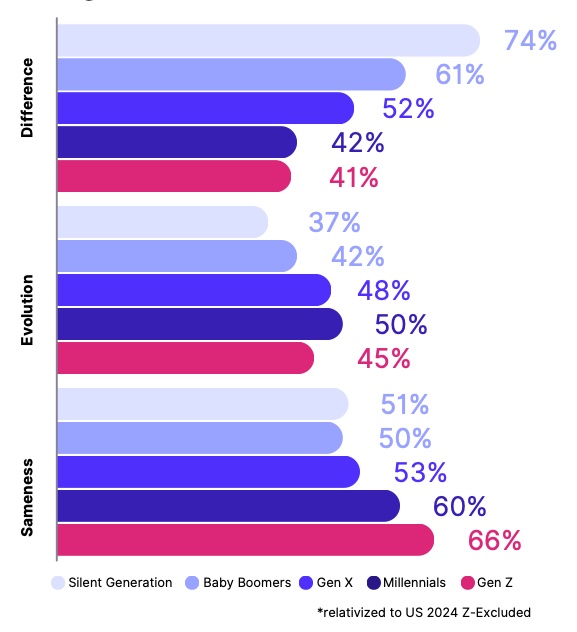
Reality: The truth is more nuanced. Across the generations, the Marlee study revealed a significant 45% drop in an appetite for newness and constant change and a 32% increase in a desire for things to stay the same at work. This suggests that Gen Z is seeking long-term security rather than being disloyal. However, they're also not afraid to leave if a workplace doesn't align with their values or provide growth opportunities.
A 45% drop in an appetite for newness and constant change
4. "Lazy and unmotivated"
This harmful stereotype suggests that Gen Z lacks a work ethic and drive.
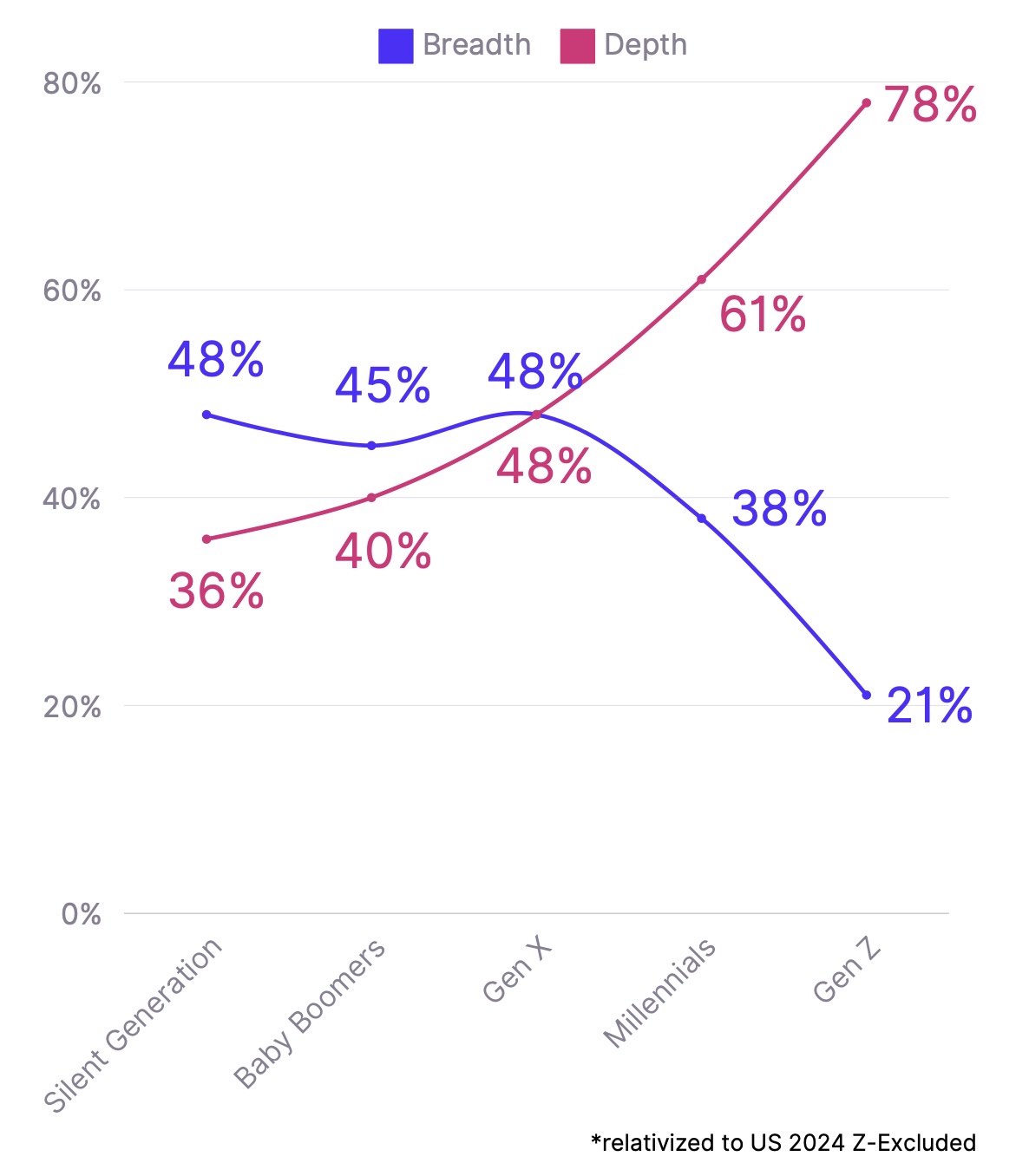
Reality: Far from being lazy, the Marlee study shows that Gen Z has a unique approach to work. One of the most significant findings in the study that impacts how the generations align has to do with the way they conceptualize the scope of work. There’s been a 56% decrease across the generations away from ‘big picture thinking’, and a 120% increase in a focus on being detail-oriented.
Abstract goals and a lack of clarity around expectations will create a situation where Gen Z will disengage and struggle to find the motivation to stay on track. For early generations, they connect via aspiration and abstract ideas, an approach that Gen Z will struggle to adopt.
A 56% decrease in ‘big picture’ thinking across generations
Debunking the myths: Gen Z's strengths
Now that we've challenged some common stereotypes let's explore the unique strengths and motivations that Gen Z brings to the workplace:
1. Problem-solvers extraordinaire
What motivates the different generations at work has dramatically changed over time. Earlier generations are self-starters, energized by aspirational goals and clear objectives, more than a desire to find and solve problems. This trend flips with Gen X and progressively increases with Millennials and then Gen Z.
So much so, that across the generations there’s a 42% drop in the desire to jumpstart initiatives and a significant 69% rise in the propensity to predict, prevent and solve problems.
This makes Gen Z a valuable asset in identifying and addressing workplace challenges before they escalate.
For leaders: Moving so fast with your eyes on the prize means you may skip over or miss important details, especially when it comes to risks. Turn to your Gen Z teammates who have a superpower for spotting what should be avoided, minimized or removed. With your powers combined, you can carve a clearer path towards your goals and get back in flow.
A significant 69% rise in the propensity to predict, prevent, and solve problems
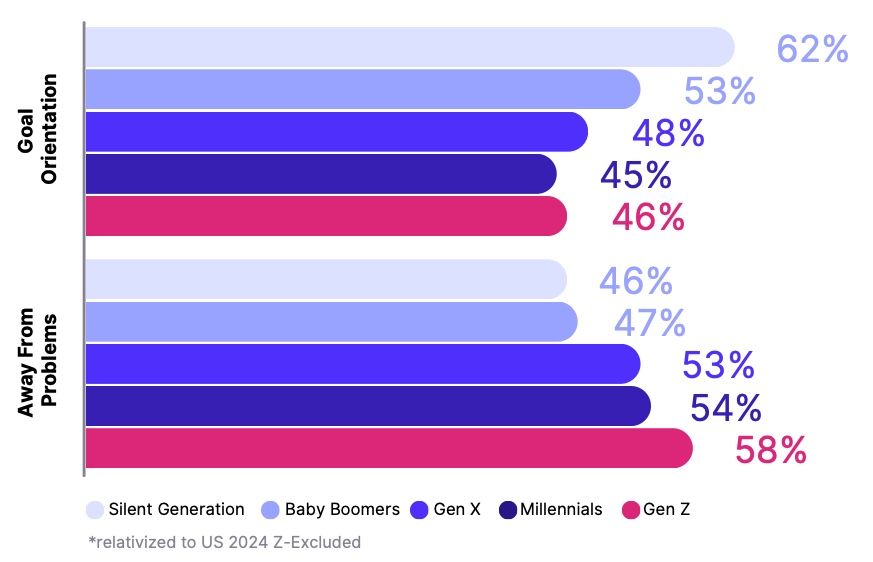
2. Detail-oriented
Contrary to stereotypes of laziness, Gen Z shows a remarkable attention to detail. The study found a 120% increase in being detail-oriented compared to earlier generations. Rather than skimming the surface, they want to dive deep into things, unsatisfied by overviews or simplistic explanations. This meticulous approach can lead to high-quality work and fewer errors.
In addition to their attention to detail, Gen Z is highly methodical. The study uncovered a 100% increase in their desire for best practices: they really care about doing things the right way at work. Coupled with a 73% drop in the importance of options and different ways of doing things, it’s the recipe for a generation that doesn’t want to waste time or resources, always seeking the most efficient ways of working.
For leaders: When collaborating with Gen Z, start by setting clear expectations and mapping out a step-by-step plan. This can give them the boost of energy and confidence they need to get work done – don’t be surprised if they take it and run with it! Lean into their natural motivation for pulling together research and information, and celebrate how their efforts contribute to the success of the work.
A 120% increase in a focus on being detail-oriented

3. Stability seekers with a purpose
While often stereotyped as job-hoppers, across the generations, the study revealed a significant 45% drop in an appetite for newness and constant change, and a 32% increase in a desire for things to stay the same at work.
Workplaces need to create a culture of stability first and foremost, one marked by supervision and support, so that Gen Z feels comfortable enough to hear different perspectives and move with the winds of change. This combination can lead to long-term loyalty when companies provide stability and purpose.
A 32% increase in a desire for things to stay the same at work

The digital natives: Unlocking Gen Z's strengths
Gen Z's digital nativity is often viewed as a potential weakness, but when leveraged correctly, it can be a significant strength:
- Tech fluency: Their innate understanding of technology makes them quick adopters of new tools and platforms, potentially increasing workplace efficiency.
- Digital communication skills: While they may prefer digital communication, this skill is increasingly valuable in our globalized, often remote, work environments.
- Information literacy: Growing up with access to infinite information has made many Gen Z workers skilled at quickly finding and verifying information.
To unlock these strengths, workplaces can:
- Implement reverse mentoring programs where Gen Z employees share their digital knowledge with older colleagues.
- Utilize collaborative digital tools that play to Gen Z's strengths while fostering teamwork.
- Provide clear, step-by-step frameworks for tasks, as the Marlee study found Gen Z has a 100% increase in desire for best practices compared to earlier generations.
Bridging the generational gap: Creating an inclusive work environment
To create a workplace where Gen Z can thrive alongside other generations:
- Emphasize clear communication: Gen Z values clarity and detail. Provide clear expectations and regular feedback. Adapt your communications by using Marlee’s compare generations boards. Answer questions about your work motivations and instantly compare your results with generational trends. Access personalized, real-time data for yourself and your team, bringing this research to life in your own context.
- Foster an inclusive culture: Leverage Gen Z's natural inclination towards inclusivity to create a welcoming environment for all.
- Provide growth opportunities: Offer continuous learning opportunities to satisfy Gen Z's desire for feedback and improvement.
🌟 Explore Marlee's scalable AI-powered coaching programs to attract, engage, and retain your Gen Z team members. - Balance structure and flexibility: While Gen Z appreciates structure, they also value a flexible work environment. Strive to provide both.
The future workforce: Embracing Gen Z's potential
As we look to the future, Gen Z is poised to contribute significantly to the workforce. Their problem-solving abilities, attention to detail, commitment to inclusivity, and desire for continuous improvement are valuable assets in the workplace.
By moving beyond stereotypes and embracing Gen Z's unique strengths, organizations can create more dynamic, inclusive, and effective workplaces. The key is to view generational differences not as obstacles but as opportunities for mutual learning and growth.
As we continue to welcome Gen Z into the workforce, let's commit to seeing them for who they truly are: a generation of passionate, detail-oriented problem-solvers ready to take on the challenges of tomorrow. By doing so, we're not just benefiting Gen Z – we're creating a more robust, adaptable, and innovative future for all generations in the workplace.
👉 Download the full report: Unlocking Gen Z at Work: A Generational Impact Study 2024

